Maggot therapy
Maggot therapy is also known as maggot debridement therapy (MDT), larval therapy, larva therapy, larvae therapy,biodebridement or biosurgery. It is a type of biotherapy involving the introduction of live, disinfected maggots (fly larvae) into the non-healing skin and soft tissue wound(s) of a human or animal for the purpose of cleaning out the necrotic (dead) tissue within a wound (debridement) and disinfection. It was long believed that the debridement was selective on necrotic tissue, but new literature has questioned that belief. A recent clinical study in France showed non-selectivity of maggot action as wound surface increased over treatment.
Contents
History
Tales and early history
Written records have documented that maggots have been used since antiquity as a wound treatment. There are reports of the use of maggots for wound healing by MayaNative Americans and Aboriginal tribes in Australia. There also have been reports of the use of maggot treatment in Renaissance times. Military physicians have observed that soldiers whose wounds had become colonized with maggots experienced significantly less morbidity and mortality than soldiers whose wounds had not become colonized. These physicians included Napoleon’s general surgeon, Baron Dominique Larrey. Larrey reported during France's Egyptian campaign in Syria, 1798–1801, that certain species of fly consumed only dead tissue and helped wounds to heal.
Dr. Joseph Jones, a ranking Confederate medical officer during the American Civil War, is quoted as follows, "I have frequently seen neglected wounds ... filled with maggots ... as far as my experience extends, these worms eat only dead tissues, and do not injure specifically the well parts." The first therapeutic use of maggots is credited to a second Confederate medical officer Dr. J.F. Zacharias, who reported during the American Civil War that, "Maggots ... in a single day would clean a wound much better than any agents we had at our command ... I am sure I saved many lives by their use." He recorded a high survival rate in patients he treated with maggots.
During World War I, Dr. William S. Baer, an orthopedic surgeon, recognized on the battlefield the efficacy of maggot colonization for healing wounds. He observed one soldier left for several days on the battlefield who had sustained compound fractures of the femur and large flesh wounds of the abdomen and scrotum. When the soldier arrived at the hospital, he had no signs of fever despite the serious nature of his injuries and his prolonged exposure to the elements without food or water. When his clothes were removed, it was seen that "thousands and thousands of maggots filled the entire wounded area." To Dr. Baer's surprise, when these maggots were removed "there was practically no bare bone to be seen and the internal structure of the wounded bone as well as the surrounding parts was entirely covered with most beautiful pink tissue that one could imagine." This case took place at a time when the death rate for compound fractures of the femur was about 75–80%
Case studies and modern use
While at Johns Hopkins University in 1929, Dr. Baer introduced maggots into 21 patients with intractable chronic osteomyelitis. He observed rapid debridement, reductions in the number of pathogenic organisms, reduced odor levels, alkalinization of wound beds, and ideal rates of healing. All 21 patients' open lesions were completely healed and they were released from the hospital after two months of maggot therapy.
After the publication of Dr. Baer's results in 1931 maggot therapy for wound care became very common, particularly in the United States. The Lederle pharmaceutical company commercially produced "Surgical Maggots", larvae of the green bottle fly, which primarily feed on the necrotic (dead) tissue of the living host without attacking living tissue. Between 1930 and 1940, more than 100 medical papers were published on maggot therapy. Medical literature of this time contains many references to the successful use of maggots in chronic or infected wounds including osteomyelitis, abscesses, burns, sub-acute mastoiditis, and chronic empyema
More than 300 American hospitals employed maggot therapy during the 1940s. The extensive use of maggot therapy prior to World War II was curtailed when the discovery and growing use of penicillin caused it to be deemed outdated. Due to the lack of conventional medicines, maggot therapy was used by Allied military medical staff in Japanese prisoner of war camps in the Far East throughout World War II.
Reintroduction – more case studies
With the advent of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, Dr. Ronald Sherman, a physician previously at the University of California, Irvine, sought to re-introduce maggot therapy into thearmamentarium of modern medical care. In 1989, he set up fly breeding facilities at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Long Beach, California in order to use maggots for the treatment of wounds. Using a Paralyzed Veterans of America grant, he initiated a prospective controlled clinical trial of maggot therapy for spinal cord patients with pressure ulcers who had failed two or more courses of conventional wound care
Over 50 scientific papers have been published that describe the medical use of maggots. Six thousand maggot therapy patients have been included in case histories or other studies. About 400 patients have been documented within clinical studies, most of them are included in a British study financed by the NHS.
Limb salvage rates with maggot therapy are about 40% to 50% according to the medical literature. Some report success rates of 70% to 80%, though definitions of "success" can vary
In a 2007 preliminary trial, maggots were used successfully to treat patients whose wounds were infected with MRSA, a bacterium (Staphylococcus aureus) with resistance to most antibiotics, including methicillin. Some of these strains include flesh eating bacteria causing frequent deaths upon infection of deep tissue. Maggots clean up the already dead tissue thus preventing further infection spread.
In 1995, a handful of doctors in four countries were using maggot therapy. Today, any physician in the U.S. can prescribe maggot therapy. There are over 800 health care centers in the United States that have utilized maggot therapy. Over 4,000 therapists are using maggot therapy in 20 countries. Approximately 50,000 treatments were applied to wounds in the year 2006 These data appear on the website of the Wound Care Information Network, but the original sources are not provided.
Regulation
In January 2004, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted permission to produce and market maggots for use in humans or animals as a prescription-only medical device for the following indications "For debriding non-healing necrotic skin and soft tissue wounds, including pressure ulcers, venous stasis ulcers, neuropathic foot ulcers, and non-healing traumatic or post-surgical wounds." In February 2004, the British National Health Service (NHS) permitted its doctors to prescribe maggot therapy. In theEuropean Union, Canada and Japan maggots are classified as medicinal drugs, needing a full market licence. In the U.S., maggots for medicinal use are classified as a device.
Veterinary use]
The use of maggots to clean dead tissue from animal wounds is part of folk medicine in many parts of the world. It is particularly helpful with chronic osteomyelitis, chroniculcers, and other pus-producing infections that are frequently caused by chafing due to work equipment. Maggot therapy for horses in the United States was re-introduced after a study published in 2003 by veterinarian Dr. Scott Morrison. This therapy is used in horses for conditions such as osteomyelitis secondary to laminitis, sub-solar abscesses leading to osteomyelitis, post-surgical treatment of street-nail procedure for puncture wounds infecting the navicular bursa, canker, non-healing ulcers on the frog, and post-surgical site cleaning for keratoma removal
However, there have not been many case studies done with maggot debridement therapy on animals, therefore, it can be difficult to assess how successful it is (Jones & Wall, 2007).
Application of maggot wound dressings
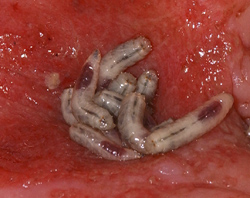
Maggots are contained in a cage-like dressing over the wound for two days. The maggots may be allowed to move freely within that cage, with the wound floor acting as the bottom of the cage; or the maggots may be contained within a sealed pouch, placed on top of the wound. The dressing must be kept air permeable because maggots require oxygen to live. When maggots are satiated, they become substantially larger and seek to leave the site of a wound. Multiple two-day courses of maggot therapy may be administered depending on the severity of the non-healing wound.Maggots can never reproduce in the wound since they are still in the larval stage and too immature to do so. Reproduction can only occur when they become adult flies and mate.
Mechanisms of action
The maggots have one principal action reported in the medical literature:
- debride wounds by dissolving necrotic (dead), infected tissue as well as vital tissue when dose is too high or time of treatment is not appropriate
Disinfection of the wound by killing bacteria and healing could not be proved by the largest clinical study available
Maggot therapy may also reduce the need for antibiotics in people with complex, chronic wounds
Maggot therapy has been shown to accelerate debridement of necrotic wounds. In about 1/3 of all patients pain is increased.
Maggot therapy is further compatible with other wound care therapies such as antibiotics, negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), skin grafting and hyperbaric oxygen therapy. While maggot therapy cannot be used simultaneously with NPWT, it can be used prior to NPWT to debride a wound so that it can be later closed with NPWT. Similarly, while maggot therapy cannot be used simultaneously with skin grafting, it can be used prior to skin grafting to debride a wound so that it can be later closed with skin grafting.
Debridement
The debridement of necrotic (dead) tissue using maggots or other methods has not been proven to provide medical benefit compared to no debridemen
In maggot therapy, large numbers of small maggots consume necrotic tissue far more precisely than is possible in a normal surgical operation, and can debride a wound in a day or two. While in the past it was believed that maggots do not damage healthy tissue, this is in doubt now Wound surface is increased on the use of maggots. They derive nutrients through a process known as "extracorporeal digestion" by secreting a broad spectrum of proteolytic enzymes that liquefy necrotic tissue, and absorb the semi-liquid result within a few days. In an optimum wound environment maggots molt twice, increasing in length from 1–2 mm to 8–10 mm, and in girth, within a period of 3–4 days by ingesting necrotic tissue, leaving a clean wound free of necrotic tissue when they are removed. When they stay longer or too many are used, healthy tissue is removed as well.
Disinfection
Any wound infection is always a serious medical complication. Infected living tissue cannot heal. If the wound is infected with an antibiotic-resistant bacterial strain, it becomes difficult or impossible to treat the underlying infection and for any healing to occur. Wound infection could further be limb- and life-threatening. When maggots successfully debride a necrotic wound, the source of wound infection is usually removed; however, a health technology assessment conducted by the Department of Health Sciences of University of York found no statistically significant evidence for this
Maggot secretions are also effective against some antibiotic-resistant bacteria and have been shown to possess potent antimicrobial activity in early experimental studies from the 1930s. As early as 1957, a specific antibiotic factor was found in maggot secretions and published in the journal Nature. Secretions believed to have broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity include allantoin, urea, phenylacetic acid, phenylacetaldehyde, calcium carbonate, proteolytic enzymes, and many others. Bacteria not killed by these secretions are subsequently ingested and lysed within the maggots.[citation needed]
In vitro studies have shown that maggots inhibit and destroy a wide range of pathogenic bacteria including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), group A and B streptococci, and Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic strains Therefore maggot therapy might represent a cost-effective method for managing MRSA infection. Other bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa, E.coli or Proteus spec are not attacked by maggots and in case of Pseudomonas even the maggots are in danger. Consequently, using maggots alone might lead to a change of bacteria cultures on the wound.
Wound healing
Maggot therapy has been expected from case studies to have wound healing properties. Two European clinical studies show that healing cannot be expected by maggots.
Limitations
The wound must be of a type which can actually benefit from the application of maggot therapy. A moist, exudating wound with sufficient oxygen supply is a prerequisite. Not all wound-types are suitable: wounds which are dry, or open wounds of body cavities do not provide a good environment for maggots to feed. In some cases it may be possible to make a dry wound suitable for larval therapy by moistening it with saline soaks, applied for 48 hours.
Maggots have a short shelf life which prevents long term storage before use Patients and doctors may find maggots distasteful, although studies have shown that this does not cause patients to refuse the offer of maggot therapy Maggots can be enclosed in opaque polymer bags to hide them from sight. Dressings must be designed to prevent any maggots from escaping, while allowing air to get to the maggots. Dressings are also designed to minimize the uncomfortable tickling sensation that the maggots often cause.
Comparative studies
In 2008, a scientific study published in the British Medical Journal compared the merits of maggot therapy and standard hydrogels to treat 270 British patients with leg ulcers from around the UK. Patients were treated with either maggots or hydrogel and their progress followed for up to a year.
The study revealed no significant differences in the time taken for the ulcer to heal, or in the patient's quality of life. Maggots were shown to be no more effective than hydrogel treatment at reducing the amount of bacteria present or in clearing MRSA. Although maggots were significantly more efficient at debridement of the wound, treatment with maggots was associated with more pain by patients. A separate study which compared the relative cost-effectiveness of maggot therapy with hydrogels estimated there was little to choose between the two therapies
In a 2011 study of people with non-healing wounds, maggot therapy was more effective in debriding than conventional surgical wound-cleaning during the first week, but there was no significant added benefit by day 15 Surprisingly, wounds debrided by maggots showed significantly increased wound surface compared to surgical debridement "Moreover, the second week of treatment could be deleterious because a significant increase in wound surface area at day 15 in the MDT group was observed"
Biology of flies and maggots used in maggot therapy
Maggots are fly larvae, or immature flies, just as caterpillars are butterfly or moth larvae. Not all species of flies are safe and effective as medicinal maggots. There are thousands of species of flies, each with its own habits and life cycle. Some fly larvae feed on plants or animals, or even blood. Others feed on rotting organic material.
Those flies whose larvae feed on dead animals will sometimes lay their eggs on the dead parts (necrotic or gangrenous tissue) of living animals. The infestation by maggots of live animals is called "myiasis." Some maggots will feed only on dead tissue, some only on live tissue, and some on live or dead tissue. The flies used most often for the purpose of maggot therapy are "blow flies" (Calliphoridae); and the species used most commonly is Lucilia sericata, the common green bottle fly. Another important species, Protophormia terraenovae, is also notable for its feeding secretions, which combat infection by Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus pneumoniae.[34]
All maggots used for debridement are specialized and grown in a laboratory setting. This ensures that the larvae are sterilized in order to prevent secondary infections caused by microbes carried in by the maggots. Due to their short lifespan, usability is limited. This means that shipment must be direct and over night. They are also sensitive to temperature variations and must be transported with great care. Some of these challenges have limited the use of maggot therapy in certain regions of the world.
In popular culture
In Bernard Cornwell's novel Sharpe's Eagle, set in 1810, the wound of Lt. Sharpe is left clean by applied maggots. In its TV adaptation, rather than being merely discussed, the maggots are shown on the skin around the wound.- In an episode of Chicago Hope a patient undergoes maggot therapy. The maggots are not shown though.
- In the 2000 film Gladiator, Russell Crowe's character has a shoulder wound cleaned with maggots.
- In the young adult novel The Dolphins of Laurentum, taking place in Roman Italy, maggots were used on an injury as an alternative to amputation. In the story the therapy was successful and the man was able to walk again.
- In addition, the television show House, M.D. included treatment of a burn by maggot therapy in the twelfth episode of the second season, titled "Distractions," on February 14, 2006.
- Claire Fraser, a medical practitioner and principal character in Diana Gabaldon's Outlander series of novels, often uses maggots for debridement of necrotic tissue in her patients' wounds.
- The titular character of Johnny Got His Gun claims that maggot therapy could have prevented his quadruple amputations.
- In her 2009 novel The Year of the Flood, Margaret Atwood focuses on a group called God's Gardeners, a small community of survivors of the same environmental catastrophe who are using maggot therapy for many acute wounds.
- In the American Dad season 9 episode "Killer Vacation", Steve mentions maggot therapy when his friend suggests using bees to clean his open wound.
- In Ken Burns's 2007 WWII documentary The War, Earl Burke, a B17 ball turret gunner, describes maggot therapy debridement of his osteomyelitis infection from a wound sustained in action.
- Dr. Gene Porter, small town doctor, father of Rachel Matheson in NBC's sci-fi drama Revolution uses maggots to help heal the infection in Miles's arm in episode s02e10
.



No comments:
Post a Comment